The Latest News
FCC | Broadband | Wireless | Congress
NTIA Approves BEAD Program Initial Proposals For Kansas, Nevada, & West Virginia
April 25, 2024 – The National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has approved Kansas, Nevada, and West Virginia’s Initial Proposals for the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) Program. The Initial Proposals detail how each state plans to spend their BEAD allocation by providing grants to deploy high-speed broadband to all unserved and underserved locations within their borders. Kansas, Nevada, and West Virginia may now request access to funding and begin implementation of their BEAD broadband grant programs. However, all are awaiting NTIA approval of the results of their challenge processes. The three states were allocated the following amounts under BEAD: Kansas – $451.7 million; Nevada – $416.6 million; and West Virginia – $1.2 billion. All states submitted their Initial Proposals by December 27, 2023. NTIA will continue to announce approval of Initial Proposals on a rolling basis. Updates on the status of other U.S states and territories’ Initial Proposals are available online from NTIA’s Bead Initial Proposal Progress Dashboard page.
FTC Approves Rule Banning Noncompete Agreements For All Workers
April 23, 2024 – The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has issued a final rule that bans noncompete agreements for all workers on a nationwide basis. Noncompete agreements impose contractual conditions that prevent workers from taking a new job or starting a new business, and often force workers to stay in a job they want to leave. The FTC estimates that 30 million workers are subject to a noncompete. The final rule banning noncompete agreements and clauses will become effective 120 days after it is published in the Federal Register. The FTC has released an outline that provides the following high-level overview of the rule:
The final rule bans new noncompetes with all workers, including senior executives after the effective date.
For existing noncompetes, the final rule adopts a different approach for senior executives than for other workers. For senior executives, existing noncompetes can remain in force. Existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives are not enforceable after the effective date of the final rule.
The FTC estimates that banning noncompetes will result in: Reduced health care costs: $74-$194 billion in reduced spending on physician services over the next decade; New business formation: 2.7% increase in the rate of new firm formation, resulting in over 8,500 additional new businesses created each year; and Rise in innovation: an average of 17,000-29,000 more patents each year for the next ten years.
Altice USA, Inc. Affiliates Default On RDOF Awards In Arkansas, Kentucky, & West Virginia
April 19, 2024 – Altice USA, Inc.’s affiliates TCA Communications, LLC, Cebridge Telecom KY, LLC, and Cebridge Telecom WV, LLC have notified the Federal Communications Commission that they are defaulting on their Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) awards in 22 census block groups (CBGs) in Arkansas, Kentucky, and West Virginia. The Altice companies were awarded RDOF funding to deploy 100/20 Mbps broadband service. In the letter notifying the FCC of their failure to try and meet their obligations, the Altice companies provided the following explanation:
Altice is committed to closing the digital divide and delivering high-speed broadband to rural communities, including through expansion of its broadband network in Arkansas, Kentucky, and West Virginia, and had begun connecting unserved locations in some of these RDOF areas. By relinquishing these CBGs now, however, Altice helps ensure that unserved and underserved locations in these areas are eligible to receive federal funding through programs like NTIA’s Broadband Equity Access and Deployment (“BEAD”) Program. These states are in the process of finalizing their BEAD eligibility maps and removing the below CBGs as federally-funded with enforceable commitments will permit unserved and unserved locations in these areas to receive even higher speeds.
FCC Final Agenda For April 25th Open Meeting – Net Neutrality Order
April 18, 2024 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has set the final agenda for its open meeting on Thursday, April 25, 2024:
Implementation of the National Suicide Hotline Act of 2018 – The Commission will consider a Second Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, which would propose to require the implementation of one or more georouting solutions for wireless calls to the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline to ensure that calls are routed based on the geographic location for the origin of the call, rather than the area code and exchange associated with a wireless phone. (WC Docket No. 18-336)
Safeguarding and Securing the Open Internet; Restoring Internet Freedom – The Commission will consider a Declaratory Ruling, Order, Report and Order, and Order on Reconsideration that would reestablish the Commission’s authority to protect consumers and safeguard the fair and open Internet by classifying broadband Internet access service as a telecommunications service and classifying mobile broadband Internet access service as a commercial mobile service; exercising broad and tailored forbearance; and reinstating straightforward, clear rules to ensure Internet openness. (WC Docket No. 23-320)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
FCC Announces Defaulted RDOF & CAF II Census Block Groups Eligible For Other Funding Programs
April 15, 2024 – The FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau has released a Public Notice announcing that certain Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) and Connect America Fund (CAF) Phase II auction census block groups (CBGs) are now eligible for other funding programs. The following three providers have defaulted on winning RDOF and CAF II bids, making the relevant CBGs eligible for other funding:
RiverStreet Communications of North Carolina, Inc. (Study Area Code 239033) has notified the FCC that it will not fulfill its commitment to offer voice and broadband service to certain CBGs within its CAF Phase II auction supported service area in North Carolina.
Cebridge Telecom LA, LLC (Study Area Code 279064) has notified the FCC of its decision to withdraw from the RDOF support program in all the CBGs covered by its authorized winning bids in Louisiana.
Cable One VoIP LLC d/b/a Sparklight (Study Area Code 279065) has notified the FCC of its decisions to withdraw from the RDOF support program in all the CBGs covered by its authorized winning bids in Louisiana.
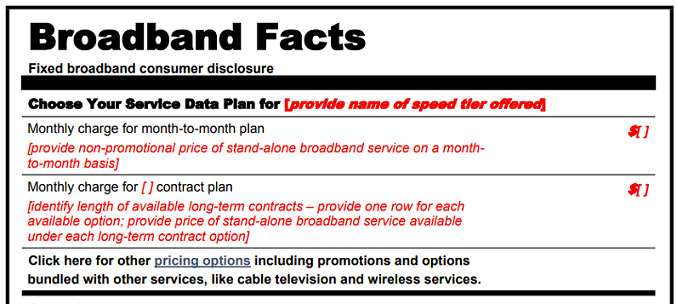
Large ISPs Now Required To Display Broadband Consumer Labels
April 10, 2024 – Starting today, large Internet service providers (ISPs) are required to display broadband consumer labels for online and in-store points of sale. In a 2022 Report And Order, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) adopted rules requiring “ISPs to display, at the point of sale, labels that disclose certain information about broadband prices, introductory rates, data allowances, and broadband speeds, and to include links to information about their network management practices, [and] privacy policies.” Broadband consumer labels resemble nutrition labels that appear on food products. The FCC adopted one label requiring the same information and in the same format for both fixed and mobile broadband service offerings. ISPs with 100,000 or fewer subscribers are required to begin displaying broadband labels by October 10, 2024. Additionally, by October 10, 2024, all ISPs “will be required to make their broadband labels machine-readable to enable third parties to more easily collect and aggregate data for the purpose of creating comparison-shopping tools for consumers.”
Senator Cantwell & Representative McMorris Rodgers Release Draft Version Of Comprehensive Privacy Law
April 7, 2024 – U.S. Senator Maria Cantwell (D-WA), Chair of the Senate Committee on Commerce, Science and Transportation, and U.S. Representative Cathy McMorris Rodgers (R-WA), Chair of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce, have released the American Privacy Rights Act, a draft version of a comprehension privacy law. The discussion draft legislation would replace the patchwork of state laws with a single national privacy standard, and restrict the amount of data that “companies can collect, keep and use about people, of any age,” while also creating a private right of action for privacy violation. The discussion draft of the American Privacy Rights Act and a section-by-section summary are available online.
FCC Tentative Agenda For April Open Meeting Contains Net Neutrality Order
April 4, 2024 – Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting scheduled for Thursday, April 25, 2024:
Promoting a Fast, Open, and Fair Internet – The Commission will consider a Declaratory Ruling, Order, Report and Order, and Order on Reconsideration that would reestablish the Commission’s authority to protect consumers and safeguard the fair and open Internet by classifying broadband Internet access service as a telecommunications service and classifying mobile broadband Internet access service as a commercial mobile service; exercising broad and tailored forbearance; and reinstating straightforward, clear rules to ensure Internet openness. (WC Docket No. 23-320)
Georouting for the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline – The Commission will consider a Second Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, which would propose to require the implementation of one or more georouting solutions for wireless calls to the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline to ensure that calls are routed based on the geographic location for the origin of the call, rather than the area code and exchange associated with a wireless phone. (WC Docket No. 18-336)
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
March 2024
CISA Announces Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act Rulemaking Will Begin April 4, 2024
March 27, 2024 – The U.S. Department Of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has announced it will publish a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) to implement the Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act (CIRCIA) on April 4, 2024. CIRCIA, signed into law in 2022, requires covered entities in the critical infrastructure sector to report covered cyber incidents and ransom payments to CISA within prescribed timeframes. CISA has released a 447-page draft version of the NPRM and proposed rules that is available online. Once the proposed rules are officially published in the Federal Register, responsive comments and related material will be due within 60 days. CIRCIA requires CISA to adopt final rules within 18 months of publishing the NPRM.
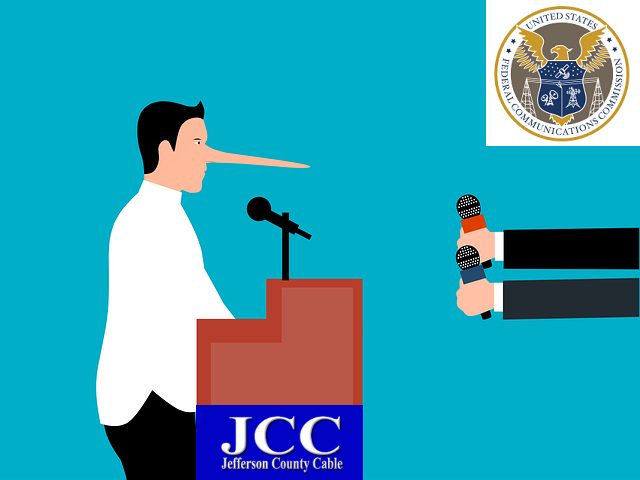
FCC Fines Jefferson County Cable TV Inc. $10,000 For Fraudulent Broadband Deployment Reporting In Ohio
March 15, 2024 – The FCC’s Enforcement Bureau has entered into a Consent Decree with Jefferson County Cable TV Inc. which resolves an investigation into whether the company reported false broadband deployment data to the FCC. Jefferson County Cable will pay a $10,000 civil penalty to the U.S. Treasury and implement a compliance plan to ensure it follows the FCC’s Broadband Data Collection rules. The Enforcement Bureau’s investigation concerned Jefferson County Cable’s two Broadband Data Collection submissions showing broadband service availability in 2022:
In an August 2022 broadband data filing showing deployment as of June 30, 2022, Jefferson County Cable reported 8,178 addresses to the FCC’s Broadband Data Collection; and
In a March 2023 broadband data filing showing deployment as of December 31, 2022, Jefferson County Cable reported 6,605 addresses to the FCC’s Broadband Data Collection.
The Enforcement Bureau began investigating after “an individual challenged Jefferson County Cable about its claim that it could provide broadband service at a location in Bergholz, Ohio.” Ultimately, Jefferson County Cable corrected its submissions covering 2022 deployment data by removing approximately 1,500 locations. In a response to the Bureau’s letter of inquiry, the company stated it “could not provide broadband service at or connect those locations within 10 business days of a request for service, as required by the Broadband Data Collection Rules.”
According to online technology publication Ars Technica, a Jefferson County Cable executive, in an email response to the individual that challenged the deployment data, admitted that the company was making false claims about service availability to block potential broadband funding being allocated in the area. The individual that made the challenge operates Smart Way Communications, a wireless Internet service provider:
Jefferson County Cable's false claim came to light thanks to Ryan Grewell, who runs a small wireless Internet service provider called Smart Way Communications. He heard about the false claims from his own customers and used the FCC's map system to file challenges at specific addresses.
One of Grewell's challenges at an address in Bergholz, Ohio, led to the cable company admitting its false claims. Last week's FCC order said this address was one of the 1,500 incorrectly claimed locations.
As we reported, Grewell got a response from a Jefferson County Cable executive who mistakenly thought Grewell was a potential customer instead of a competitor. The email said that Jefferson County Cable didn't serve the area yet, but wanted to prevent potential competitors from getting deployment grants.
"You challenged that we do not have service at your residence and indeed we don't today," said the January 2023 email from Jefferson County Cable executive Bob Loveridge. "With our huge investment in upgrading our service to provide xgpon we reported to the BDC [Broadband Data Collection] that we have service at your residence so that they would not allocate addition [sic] broadband expansion money over [the] top of our private investment in our plant."
FCC Redefines Broadband As 100/200 Mbps In Latest Broadband Deployment Report
March 14, 2024 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC or Commission) has approved its latest annual Broadband Deployment Report which shows the status of fixed and mobile broadband service in the U.S. The report was approved on a 3-2 vote (FCC Chairwoman Rosenworcel, Commissioners Starks and Gomez approving, and Commissioners Carr and Simington dissenting). Most notably, the report “raises the Commission’s benchmark for high-speed fixed broadband to download speeds of 100 megabits per second and upload speeds of 20 megabits per second – a four-fold increase from the 25/3 Mbps benchmark set by the Commission in 2015.” Ultimately, the FCC concludes in the report that “advanced telecommunications capability is not being deployed in a reasonable and timely fashion based on the total number of Americans, Americans in rural areas, and people living on Tribal lands who lack access to such capability, and the fact that these gaps in deployment are not closing rapidly enough.”
Section 706(b) of the Telecommunications Act of 1996, directs the FCC to annually inquire whether advanced telecommunications capability (broadband) is being deployed to all Americans in a reasonable and timely fashion. Advanced telecommunications capability is described as high-speed, switched, broadband telecommunications capability that enables users to originate and receive high-quality voice, data, graphics, and video telecommunications using any technology. If the FCC determines that broadband is not being deployed in a timely manner, Section 706(b) requires the FCC to take immediate action to accelerate broadband deployment by removing barriers to infrastructure investment and promoting competition.
One other key item in the report is a new 1 Gbps/500 Mbps long-term goal for broadband speeds to give “a better, faster, more robust system of communication for American consumers. According to the FCC’s News Release announcing the approval, the report shows that, as of December 2022:
Fixed terrestrial broadband service (excluding satellite) has not been physically deployed to approximately 24 million Americans, including almost 28% of Americans in rural areas, and more than 23% of people living on Tribal lands;
Mobile 5G-NR coverage has not been physically deployed at minimum speeds of 35/3 Mbps to roughly 9% of all Americans, to almost 36% of Americans in rural areas, and to more than 20% of people living on Tribal lands;
45 million Americans lack access to both 100/20 Mbps fixed service and 35/3 Mbps mobile 5G-NR service; and
Based on the new 1 Gbps per 1,000 students and staff short-term benchmark for schools and classrooms, 74% of school districts meet this goal.
FCC Approves New All-In Pricing Rules For Cable And Satellite TV
March 14, 2024 – The Federal Communications Commission (FCC or Commission) has approved a Report And Order that applies new “all-in” pricing rules to cable operators and direct broadcast satellite (DBS) providers. The new rules were passed by a 3-2 vote, with Chairwoman Rosenworcel, Commissioners Starks and Gomez approving, and Commissioners Carr and Simington dissenting. The FCC News Release announcing the action describes the new rules as follows:
These new rules require cable operators and direct broadcast satellite (DBS) providers to state the total cost of video programming service clearly and prominently, including broadcast retransmission consent, regional sports programming, and other programming-related fees, as a prominent single line item on subscribers’ bills and in promotional materials. The record demonstrates that charges and fees for video programming provided by cable and DBS providers are often obscured in misleading promotional materials and bills, which causes significant and costly confusion for consumers.
USF Contribution Factor Dips To 32.8 Percent For Second Quarter Of 2024
March 14, 2024 – The FCC’s Office of Managing Director (OMD) has announced that the proposed universal service fund (USF) contribution factor for the Second quarter of 2024 will be 32.8 percent. If the FCC takes no action on the proposed USF contribution factor within 14 days, it will be declared approved. The 32.8 percent contribution factor for 2Q 2024 is a slight decrease from the 34.6 percent USF contribution factor that was used for 1Q 2024, and which is the all-time record high. Historical information on quarterly universal service fund contribution factors is available online from the FCC.
For the second quarter of 2024, the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC) projects $8.555642 billion in total interstate and international end-user telecommunications revenues will be collected ($8.313338 billion was projected for 1Q 2024). USAC estimates that $2.092510 billion is needed to cover the total demand and expenses for all Federal universal service support mechanisms (revenue requirement) in the second quarter of 2024 (the 1Q 2024 demand was estimated at $2.118730 billion). Total second quarter 2024 demand includes projected program support, administrative expenses, and true-ups and adjustments, which breaks out among the USF support mechanisms as follows:
E-Rate Schools & Libraries: $652.36 million (1Q 2024 was $634.96 million)
Rural Health Care: $170.03 million (1Q 2024 was $168.60 million)
High-Cost: $1.10091 billion (1Q 2024 was $1.09021 billion)
Lifeline: $169.21 million (1Q 2024 was $225.47 million)
Senator Cruz Releases Paper On Universal Service Fund Reform
March 6, 2024 – Senator Ted Cruz (R-TX), ranking member of the U.S. Senate Committee On Commerce, Science, And Transportation, has released a document titled “Protecting Americans From Hidden FCC Tax Hikes: A Blueprint For Universal Service Fund Reform.” The paper focuses on USF contributions and the USF’s four support mechanisms: E-Rate, Lifeline, Rural Health Care, and High Cost. Ultimately, Senator Cruz argues that “Congress must reform the USF’s structural problems, re-evaluate its component programs, and get the FCC’s spending under control.” This reform effort, according to Senator Cruz, should be guided by the following eight principles:
Put Congress back in the driver’s seat (Congress should define universal service and decide where funding goes);
Move social welfare spending on-budget (the High Cost fund should stay within the USF, but the other programs should be subject to direct congressional appropriations);
Eliminate program duplication (duplicative USF spending should be eliminated);
Stop subsidizing networks that face unsubsidized competition (companies should not receive USF support for areas served by an unsubsidized competitor);
Do not subsidize Infrastructure Investment And Jobs Act funded networks’ ongoing operational costs (ongoing support for Infrastructure Act-funded networks should not be available except in case-by-case, exceptional circumstances);
Target low-income subsidies to those who truly need them (Lifeline and ACP should at least be combined, and clear performance metrics should be develop to track the effectiveness of support);
Ensure E-Rate is truly improving education and not aggravating kids’ screen addictions (E-Rate authority is explicitly confined to classrooms, and support should truly benefit pedagogical objectives); and
Establish better controls to stop waste, fraud, and abuse (the FCC should follow GAO and IG recommendations and implement better safeguards).
Sixth Circuit To Consider Legal Challenges To New FCC Data Breach Reporting Rules
March 4, 2024 – The Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation has randomly selected the U.S. Court of Appeals For The Sixth Circuit in which to consolidate two petitions for review of the FCC’s new data breach reporting rules. One petition for review was filed by the Texas Association of Business in the Fifth Circuit and one petition for review was filed by the Ohio Telecom Association in the Sixth Circuit. The petitions for review are nearly identical, and both seek judicial review of the FCC’s data breach Order on the grounds that it “exceeds the FCC’s statutory authority; is arbitrary, capricious, and an abuse of discretion within the meaning of the Administrative Procedure Act, 5 U.S.C. §§ 701 et seq.; and is otherwise contrary to law.”
Communications Infrastructure Companies File Legal Challenge To FCC’s Digital Discrimination Rules
March 1, 2024 – The Wireless Infrastructure Association, the Power & Communications Contractors Association, and NATE: The Communications Infrastructure Contractors Association have filed a petition for review of the FCC’s Order adopting digital discrimination rules. The group is challenging the digital discrimination Order by claiming it exceeds the FCC’s statutory authority, is arbitrary, capricious, and an abuse of discretion, and is otherwise contrary to law. The group filed their petition in the U.S. Court Of Appeals For The District Of Columbia Circuit, but have notified the court that the petition should be transferred to the Eight Circuit. Numerous petitions for review of the FCC’s digital discrimination rules were already filed in multiple circuits, resulting in the U.S. Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation randomly selecting the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit to hear the case.
NTIA Releases Limited Build America, Buy America Waiver For BEAD Program Covering Non-Optic Glass Inputs On Fiber And Certain Construction Materials
March 1, 2024 – The National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) has published a final limited waiver of the Build America, Buy America rules that will be available for the entirety of the Broadband Equity, Access and Deployment (BEAD) program. NTIA’s Buy America waiver covers non-optic glass inputs on fiber and certain construction materials. NTIA declined to adopt a waiver covering the entire optical fiber production process or a blanket waiver for non-U.S. country-of-origin fiber. NTIA found that non-optic glass inputs make up a minor element of the overall cost of a finished fiber optic cable, and the waiver will help ensure the availability of a secure, diverse supply of optical fiber and fiber optic cable for the duration of the BEAD program.
February 2024
NIST Releases Cybersecurity Framework Version 2.0
February 26, 2024 – The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has released version 2.0 of its Cybersecurity Framework. According to NIST, the updated version “is designed for all audiences, industry sectors and organization types, from the smallest schools and nonprofits to the largest agencies and corporations – regardless of their degree of cybersecurity sophistication.” The first version of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework was focused on the protection of critical infrastructure, and was released in 2014. It was updated to version 1.1 in 2018. The Cybersecurity Framework version 2.0, along with numerous supplementary resources are available online from NIST.
FCC Chair Releases Tentative Agenda For March 14th Open Meeting, Includes Cybersecurity Labeling Program & Section 706 Report
February 22, 2024 – Federal Communications Commission Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel has announced the following tentative agenda for the FCC’s next open meeting scheduled for Thursday, March 14, 2024:
Cybersecurity Labeling Program for Smart Products – The Commission will consider a Report and Order to create a voluntary cybersecurity labeling program for wireless consumer Internet of Things (IoT) products, which would help consumers make informed purchasing decisions, differentiate trustworthy products in the marketplace, and create incentives for manufacturers to meet higher cybersecurity standards. (PS Docket No. 23-239)
Re-Defining ‘High-Speed’ Internet to Match Market Realities – The Commission will consider the draft 2024 Section 706 Report, which, if adopted, would fulfill the Commission’s statutory responsibility under section 706 of the Telecommunications Act of 1996 and raise the fixed speed benchmark for advanced telecommunications capability to 100/20 Mbps. (GN Docket No. 22-270)
Single Network Future: Supplemental Coverage from Space – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would advance the Commission’s vision for a single network future in which satellite and terrestrial networks work seamlessly together to provide coverage for consumer handsets that neither network can achieve on its own. (GN Docket No. 23-65; IB Docket No. 22-271)
‘All-In’ Cable and Satellite TV Pricing – The Commission will consider a Report and Order to require cable and satellite TV providers to specify the “all-in” price for video programming services in promotional materials and on subscribers’ bills in order to allow consumers to make informed choices. (MB Docket No. 23-203)
‘Missing and Endangered Persons' Emergency Alert Code – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would propose to facilitate the more efficient and widespread dissemination of alerts and coordinated responses to incidents involving missing and endangered persons, an issue that is particularly prevalent in Tribal communities. (PS Docket Nos. 15-91, 15-94)
FCC Enforcement Bureau Removes 12 Companies From Robocall Mitigation Database – Intermediate Providers And Voice Service Providers Must Cease Accepting Their Traffic
February 22, 2024 – The FCC’s Enforcement Bureau has removed the certifications of the following 12 companies from the FCC’s Robocall Mitigation Database:
Viettel Business Solutions Company;
Etihad Etisalat (Mobily);
Claude ICT Poland Sp. z o. o. dba TeleCube.PL;
Nervill LTD;
Textodog Inc. dba Textodog and Textodog Software Inc.;
Phone GS;
Computer Integrated Solutions dba CIS IT & Engineering;
Datacom Specialists;
DomainerSuite, Inc.;
Evernex SMC PVT LTD;
Humbolt Voip; and
MyTaxi Ride Inc.
The Enforcement Bureau removed the 12 companies from the FCC’s Robocall Mitigation Database because all “failed to correct their facially deficient Database certifications” or failed to otherwise demonstrate their certifications should not be removed. The following four companies are domestic voice service providers: Computer Integrated Solutions dba CIS IT & Engineering, Datacom Specialists, DomainerSuite, Inc., and Humbolt Voip. Because these four have had their certifications removed from the Robocall Mitigation Database, all intermediate providers and voice service providers must cease accepting all calls directly from those four providers.
The remaining eight companies are foreign voice service providers: Viettel Business Solutions Company (Vietnam), Etihad Etisalat (Mobily) (Saudi Arabia), Claude ICT Poland Sp. z o. o. dba TeleCube.PL (Poland), Nervill LTD (Israel), Textodog Inc. dba Textodog and Textodog Software Inc. (Canada), Phone GS (France), Evernex SMC PVT LTD (Pakistan), and My Taxi Ride Inc. (unknown nation of origin). Removal from the Robocall Mitigation Database requires all intermediate providers and voice service providers to cease accepting all calls directly from these eight providers that use U.S. North American Numbering Plan (NANP) resources in the caller ID field to send voice traffic to residential or business subscribers in the United States.
FCC Removes TELECLUB From The Robocall Mitigation Database; Intermediate Providers And Voice Service Providers Must Cease Accepting NANP Calls From TELECLUB
February 22, 2024 – The FCC’s Enforcement Bureau has removed the certification of foreign voice service provider TELECLUB from the FCC’s Robocall Mitigation Database. TELECLUB’s certification was removed because the company “failed to cure its facially deficient Database certification (Certification) or otherwise demonstrate why the Bureau should not remove its Certification from the Database following the Bureau’s October 16, 2023 Order directing it to take either one of those actions.” All intermediate providers and voice service providers must cease accepting all calls directly from TELECLUB that use U.S. North American Numbering Plan resources in the caller ID field to send voice traffic to residential or business subscribers in the United States. Additionally, TELECLUB is not allowed to refile a Robocall Mitigation Database certification not re-file a Certification without the prior approval of both the FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau and Enforcement Bureau.
FCC Announces Final Agenda For February 15th Open Meeting
February 8, 2024 – The Federal Communications Commission has released the following final agenda for its open meeting on Thursday, February 15, 2024:
Increasing the Accessibility of the Emergency Alert System (PS Docket No. 15-94) – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking intended to simplify the process for alert originators to send multilingual emergency alerts over television and radio.
Empowering Consumers to Stop Robocalls and Robotexts (CG Docket No. 02-278) – The Commission will consider a Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking to strengthen consumers’ ability to revoke consent so that it is simple and easy, codify previously adopted protections that make it simpler for consumers to revoke consent, and require that callers and texters implement requests in a timely manner. The item also proposes and seeks comment on how to apply the TCPA to robocalls and robotexts from wireless providers to their own subscribers and proposes to give consumers the ability to revoke consent and thereby stop these communications.
Expanding Opportunities for Wireless Microphone Use (ET Docket No. 21-115) – The Commission will consider a Report and Order to revise the Part 15 and 74 technical rules to permit a recently developed, and more efficient, type of wireless microphone systems.
Space Innovation; Facilitating Capabilities for In-space Servicing, Assembly, and Manufacturing, (IB Docket No. 22-271) and (IB Docket No. 22-272) – The Commission will consider a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that would propose a framework for licensing space stations engaged in in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing – or “ISAM” – operations that can support sustained economic activity in space. The goal of the proposed framework is to facilitate the development of these novel space activities and advance opportunities for innovation in the new space age.
Restricted Adjudicatory Matter – The Commission will consider a restricted adjudicatory matter from the Media Bureau.
Enforcement Bureau Action – The Commission will consider an enforcement action.
The FCC’s Thursday, February 15, 2024, Open Meeting is scheduled to commence at 10:30 a.m. in the Commission Meeting Room at the FCC’s Headquarters, located at 45 L Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. The meeting will be streamed live online at www.fcc.gov/live and on the FCC’s YouTube channel.